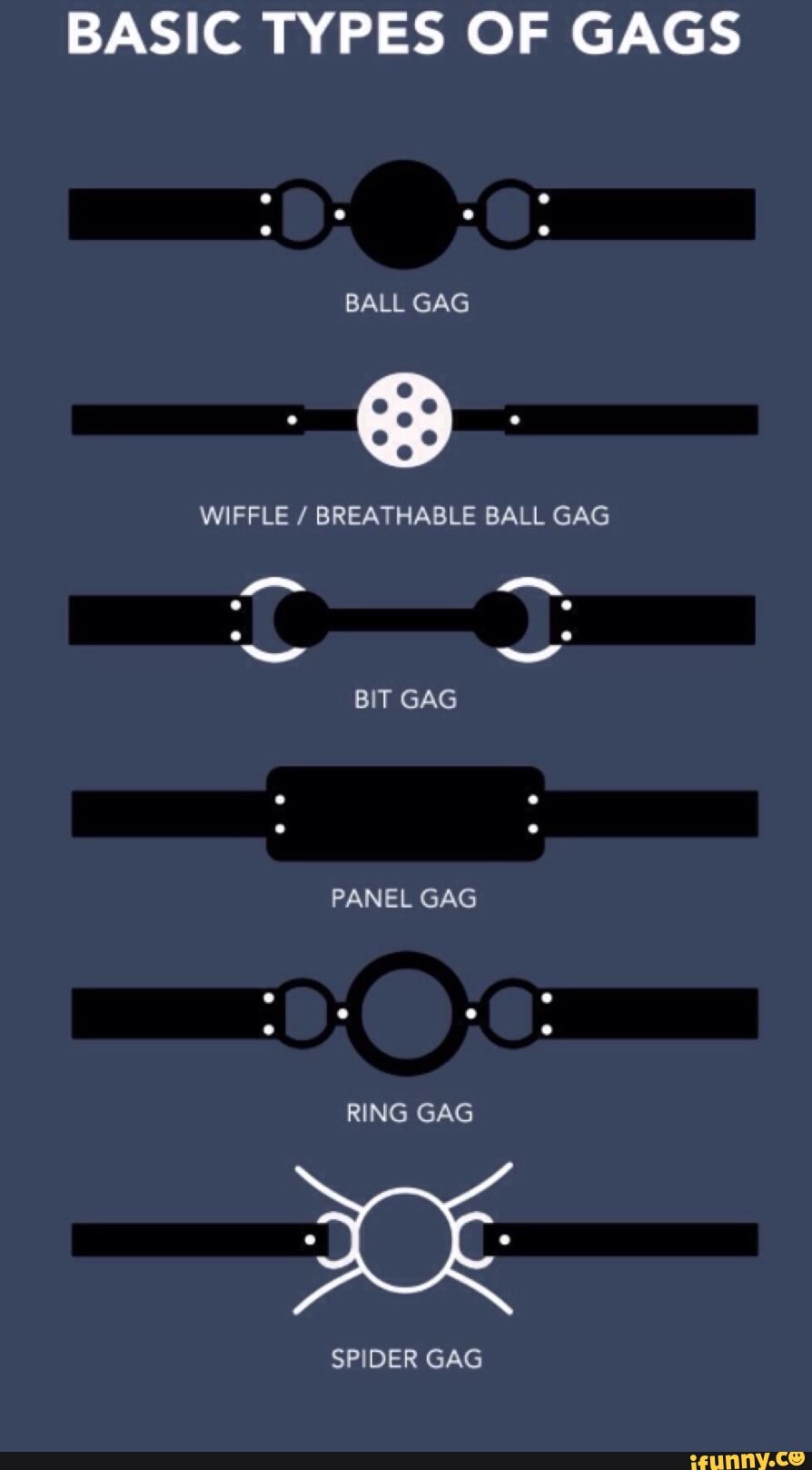
different types of gags
 Pin on A ball for gag
Pin on A ball for gagGlycosaminoglycan This article can be too technical for most readers to understand. Please, without removing the technical details. (July 2015) () may be too technical for most readers to understandGlucosaminoglycans (GAG) or mucopolysaccharides are long linears consisting of repetition units (i.e., two sugar units). The unit of two Sugar that repeats consists of one and one, with the exception of , where in the place of uronic sugar that has . Because the GAG are highly polar and attract water, they are used in the body as a lubricant or shock damper. GlycosaminoglycansGAGsmucopolysaccharides is a group in which abnormal accumulations of glucosaminoglycans are produced due to enzyme deficiencies. ContentProduction[]Glycosaminoglycans vary a lot in molecular mass, disastrous construction and sulfation. This is because GAG synthesis is not a template driven as proteins or nucleic acids, but constantly altered by processing enzymes. GAGs are classified into four groups based on nucleus disaccharide structures. / heparanoHS sulfate (GAGs) and / (CSGAGs) are synthesized in the , where the protein cores made in them are modified post-translationally with formation . can modify the kernel proteins through the proteoglycan glucose or link O. The fourth class of GAG, is synthesized by integral membrane syntase that immediately secrete the dynamically elongated disaccharide chain. heparan sulfate HSGAG and CSGAG[]HSGAG and CSGAG proteoglycans modified begin first with a Motive consensus Ser-Gly/Ala-X-Gly in the core protein. The construction of a tetrasaccharide link consisting of -GlcAβ1–3Galβ1–3Galβ1–4Xylβ1-O-(Ser)-, where , β4-galactosyl transferase (GalTI),β3-galactosyl transferase (GalT-II), and β3-GlcA transferase (Glc The addition of a GlcNAc promotes the addition of HSGAGs while the addition of GalNAc to the tetrasaccharide link promotes the development of CSGAG. GlcNAcT-I transfers GlcNAc to the linker tetrasaccahride, which is different from glicotransferase GlcNAcT-II, the enzyme used to build HSGAGs. EXTL2 and EXTL3, two genes in the family of EXT tumor suppressants, have proven to have GlcNAcT-I activity. On the contrary, GalNAc is transferred to the binding by the GalNAcT enzyme to initiate the synthesis of CSGAGs, an enzyme that may or may not have different activity compared to the GalNAc transferase activity of the condroitin synthesis. With respect to HSGAGs, a multi-merica enzyme encoded by EXT1 and EXT2 of the EXT family of genes, it transfers both GlcNAc and GlcA for HSGAG chain elongation. As it is lengthened, the HSGAG is dynamically modified, first by N-deacetillase, N-sulfotransferase (), which is a bifunctional enzyme that hangs the N-acetyl group of GlcNAc and then sulfates the N-position. Then, C-5 coated with uronyl epimerase d-GlcA to l-IdoA followed by 2-O sulfation of uronic acid sugar by sulfotransferase 2-O (). Finally, the positions of 6-O and 3-O of the GlcNAc moities are sulphated by 6-O () and 3-O (3-OST) sulfotransferases. Condroitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate, which comprise CSGAGs, differentiate between themselves by the presence of GlcA and IdoA epimers respectively. Similar to the production of HSGAGs, C-5 uronyl epimerase converts d-GlcA to l-IdoA to synthesize dermatan sulfate. Three CSGAG chain sulfation events occur: 4-O and/or 6-O GalNAc sulfation and 2-O uronic acid sulfation. Four isoforms of the GalNAc 4-O sulfotransfers (C4ST-1, C4ST-2, C4ST-3 and D4ST-1) and three isoforms of the GalNAc 6-O sulfotransfers (C6ST, C6ST-2 and GalNAc4S-6ST) are responsible for the GalNAc sulfation. Keratan sulphate types[]Unlike HSGAGs and CSGAGs, the third class of GAGs, those belonging to types of keratan sulphate, are driven towards biosynthesis through certain protein sequence motives. For example, in the cornea and cartilage, the domain of keratan sulfate consists of a series of repeated hexapeptides tandemly with an E(E/L)PFPS consensus sequence. In addition, for three other sulfated proteoglycans of keratan, , , and mimecan (), the NX(T/S) consensus sequence along with the secondary protein structure was determined to be involved in the extension of N-linked oligosaccharides with keratan sulfate. Keratan sulphate elongation begins at the non-reductive ends of three oligosaccharides of liaison, which define the three kinds of keratan sulphate. Keratan sulfate I (KSI) is N-linked via high oligosaccharide precursor hose. Keratan II sulfate (KSII) and Keratan III sulfate (KSIII) are connected to O, with KSII links identical to those of the basic structure, and KSIII linked to a 2-O mannose. Elongation of the keratan sulfate polymer occurs through the addition of Gal and GlcNAc glycosyltransferase. The addition of the Galactose occurs mainly through β-1,4-galactosyltransferase (β4Gal-T1), while the enzymes responsible for β-3-Nacetilglucosamine have not been clearly identified. Finally, polymer sulfation occurs in the 6-position of both sugar residues. The enzyme KS-Gal6ST () transfers sulfate groups to the galactose while N-acetylglucosaminyl-6-sulfotransferase (GlcNAc6ST) transfers sulfate groups to GlcNAc terminal in sulfate of keratan. Hyaluronic acid[]The fourth class of GAG, , is not sulfated and is synthesized by three sintetase transmembrane proteins, , and . HA, a linear polysaccharide, is composed of repeating disaccharide units of →4)GlcAβ(1→3)GlcNAcβ(1→ and has a very high molecular mass, from 105 to 107. Each HAS enzyme is capable of transglicosis when supplied with UDP-GlcA and UDP-GlcNAc. HAS2 is responsible for very large hyaluronic acid polymers, while smaller HA sizes are synthesized by HAS1 and HAS3. While each HAS isoform catalyzes the same biosynthetic reaction, each HAS isoform is independently active. The HAS isoforms have also proven to have different Km values for UDP-GlcA and UDPGlcNAc. It is believed that through the differences of enzyme activity and expression, the wide spectrum of biological functions mediated by the HA can be regulated, such as its participation in regulation in the subgranular zone of the brain. Function[] CSGAG interacts with heparin binding proteins, specifically sulfate dermatan interactions with FGF-2 fibroblast growth factor and FGF-7 have been involved in cell proliferation and wound repair while interactions with hepatic growth factor/stage factor (HGF/SF) activate the HGF/SF signaling pathway () through its receptor. CASGAGs are important to provide support and adhesiveness in bone, skin and cartilage. Other biological functions known to the CSGAG to perform critical functions include inhibition of growth and axonal regeneration in the development of CNS, roles in brain development, neuritógen activity and pathogenic infection. Dermatan sulfates Sulphates dermatanDermatan sulfates work on the skin, tendons, blood vessels, and heart valves. Classification[ ] The members of the glycosaminoglican family vary in the type of hexosamine, hexosa, or hexuronic acid unit they contain (e.g., , , , ). They also vary in the geometry of the . Examples of GAG are: Name Hexuronic acid orhexose (for keratan) Hexosamine Geometry of linkage between predominant monomeric units Unique features GlcUA orGlcUA(2S) GalNAc orGalNAc(4S) orGalNAc(6S) orGalNAc(4S,6S) GlcUAβ(1→3)GalNAcβ(1→4) Most prevalent GAG GlcUA orIdoUA(2S) GalNAc orGalNAc(4S) orGalNAc(6S) orGalNAc(4S,6S) 'IdoUAβ1-3'GalNAcβ1-4 Distinguished condroitin sulfate by the presence of , although some hexuronic acid monosaccharides may be . Gal orGal(6S) GlcNAc orGlcNAc(6S) -Gal(6S)β1-4GlcNAc(6S)β1-3 The Keratan type II sulfate can be. GlcUA orIdoUA(2S) GlcNAc orGlcNS orGlcNAc(6S) orGlcNS(6S) -IdoUA(2S)α1-4GlcNS(6S)α1-4 Higher negative load density of any known biological molecule GlcUA orIdoUA(2S) GlcNAc orGlcNS orGlcNAc(6S) orGlcNS(6S) -GlcUAβ1-4GlcNAcα1-4 Very similar in the structure to the heparin, however the heparan sulfate detached units are organized in different sulphate domains and not sulfated. GlcUA GlcNAc -GlcUAβ1-3GlcNAcβ1-4 The only GAG that is not exclusive ########################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################## Geometry Upstairs 7 Multiple Other Upstairs 7 Other : Unsulfated, extracellular Sulfated, extracellular Sulfated, intracellular Synthetic Navigation menu Personal tools Named spaces Variants Views More Search Navigation Contributed Tools Printing/exporting Other projects Languages

Chemical structures of the different types of GAGs used in this study.... | Download Scientific Diagram
BASIC TYPES OF GAGS WIFFLE / BREATHABLE BALL GAG - iFunny :)

Pin on Lessons in Lust

Major disaccharide repeating units of different types of GAGs (R = H or... | Download Scientific Diagram

The Structure of Glycosaminoglycans and their Interactions with Proteins - Gandhi - 2008 - Chemical Biology & Drug Design - Wiley Online Library

Pin on Lessons in Lust

Illustrations & Handouts | Horse riding tips, Horse braiding, Horse markings

Gag - Wikipedia

Horse Gag Bits | Features, Functions, Pros and Cons. - YouTube

Glycosaminoglycans and Proteoglycans | Sigma-Aldrich
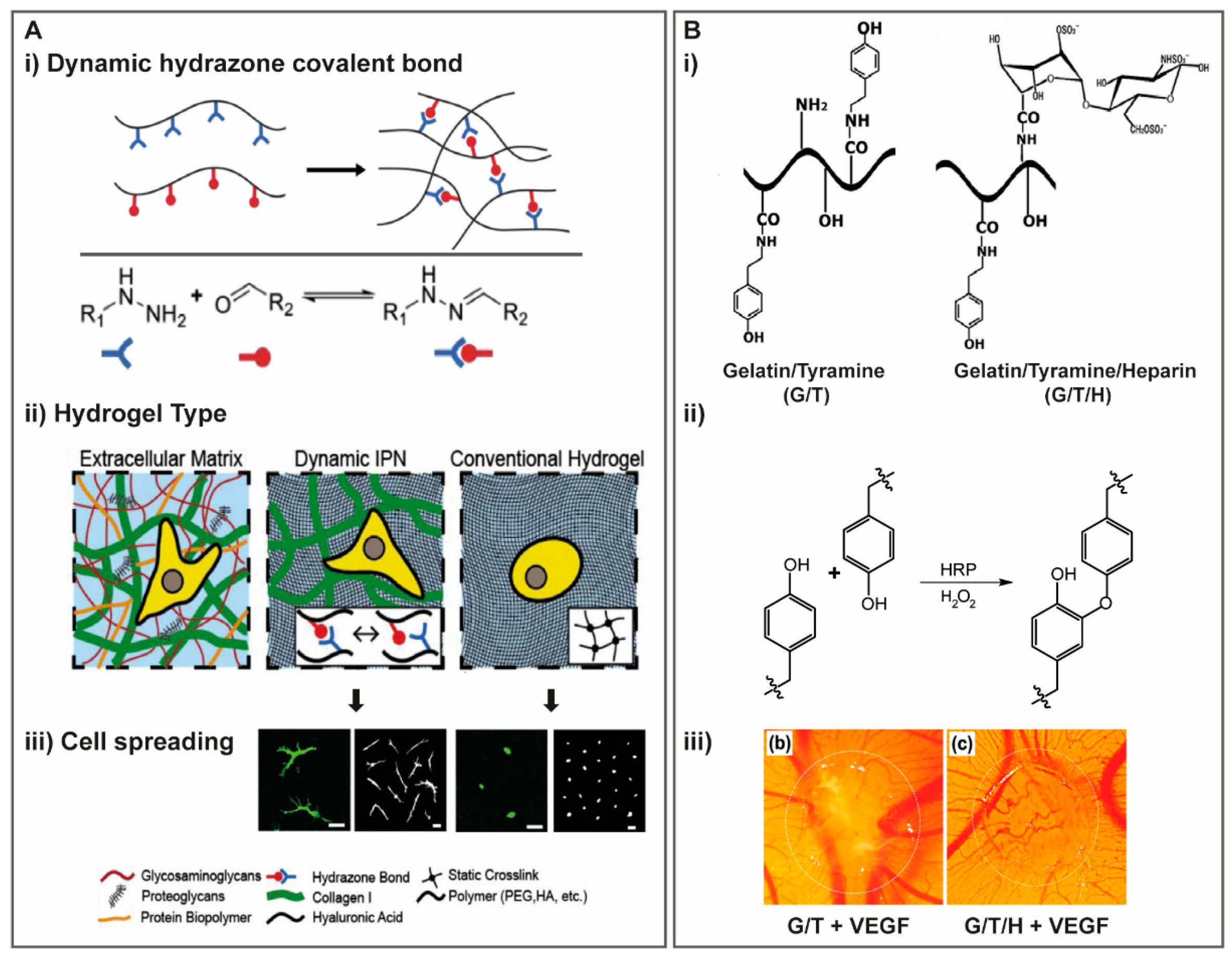
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Glycosaminoglycan-Inspired Biomaterials for the Development of Bioactive Hydrogel Networks | HTML

The story of mouth gags
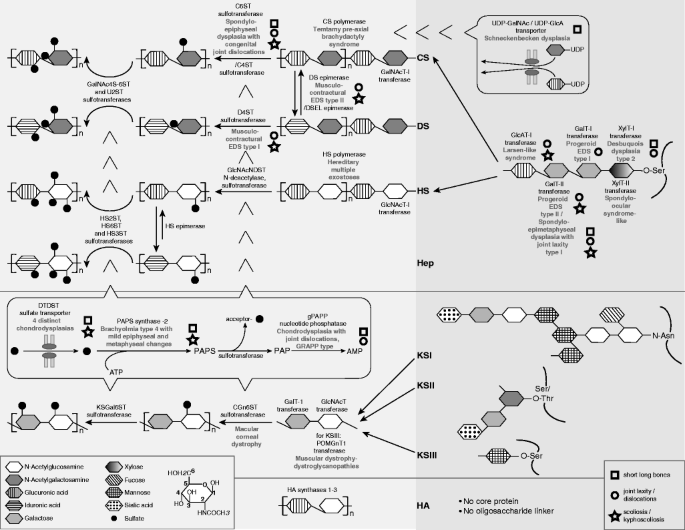
Biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycans: associated disorders and biochemical tests | SpringerLink

Glycosaminoglycan - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics

TAMSCO Mouth Gags & Retractors, All Types & Sizes 1/pk #TM-9451A

Major disaccharide repeating units of different types of GAGs (R = H or... | Download Scientific Diagram

Infographic .. Types of gags and their characteristics Sky News Arabia news | Eg24 News

The Different Types of Horse bits that can be used

Toontown

What Is a Ball Gag? - How to Use a Ball Gag - 5 Best Ball Gags
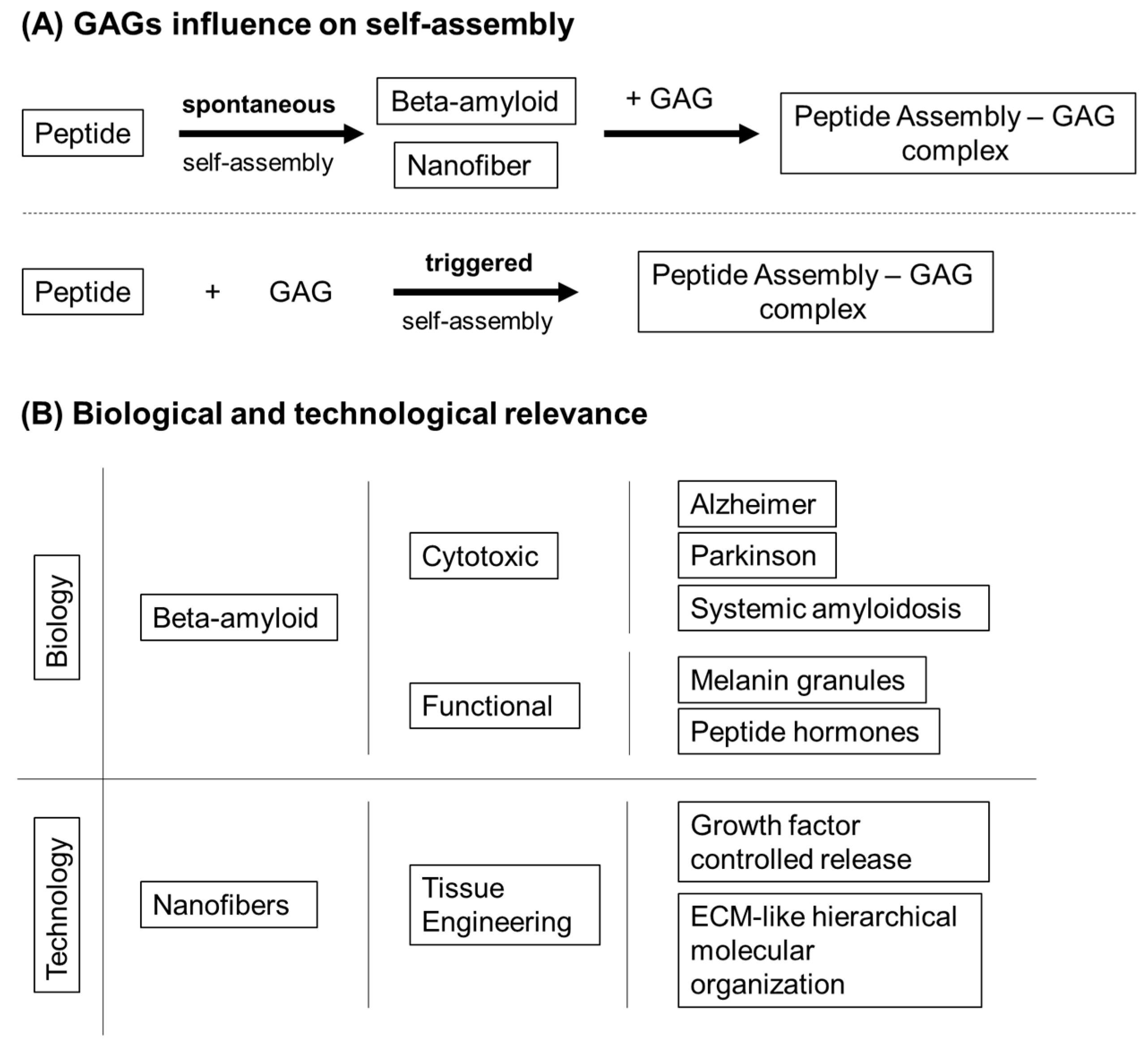
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Glycosaminoglycan-Inspired Biomaterials for the Development of Bioactive Hydrogel Networks | HTML

Various types of glycosaminoglycans | Download Table

High-resolution structures of HIV-1 Gag cleavage mutants determine structural switch for virus maturation | PNAS

So Many Gags by scarletfish8eta on DeviantArt

Chemical structures of the different types of GAGs used in this study.... | Download Scientific Diagram
28 Kinky Sex Toy Types for Beginners and Beyond: Gags, Whips, More
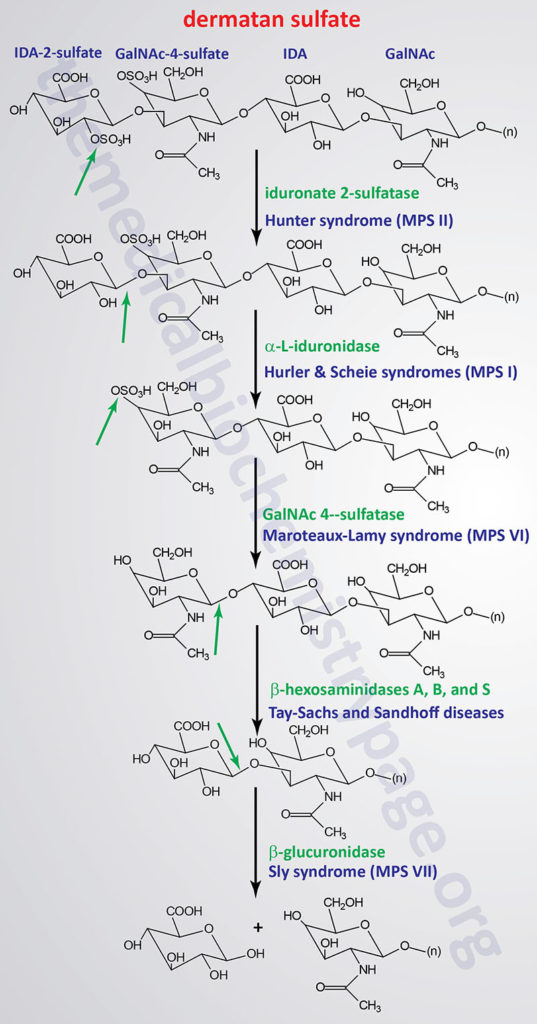
Glycosaminoglycans and Proteoglycans - The Medical Biochemistry Page

A) Classification of MPS types in correspondence to the types of GAGs... | Download Scientific Diagram
.jpg?w=840&ssl=1)
Infograph ... Types of gags and their effectiveness in preventing Corona virus - Newsy Today

What Is a Ball Gag? - How to Use a Ball Gag - 5 Best Ball Gags

Major disaccharide repeating units of different types of GAGs (R = H or... | Download Scientific Diagram
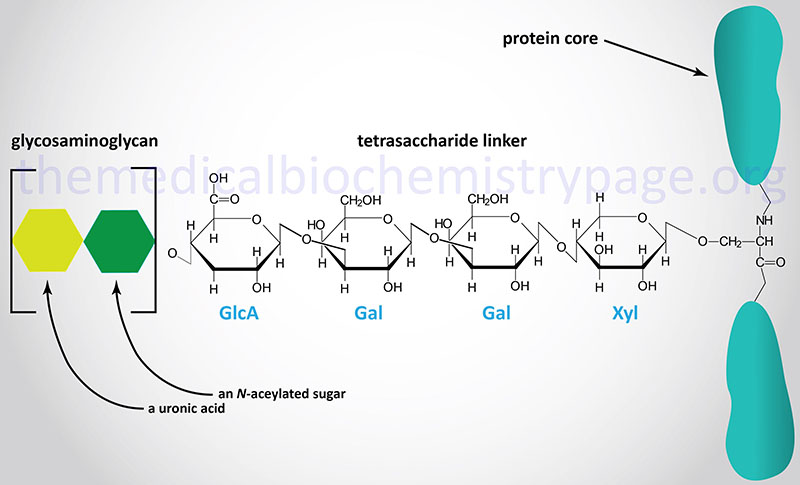
Glycosaminoglycans and Proteoglycans - The Medical Biochemistry Page

Buy Types Mouth Gags Online Shopping at DHgate.com

Tongue Forceps Mouth Gags - Tongue Forceps / Surgical Instruments - Buy Mouth Gag Medical,Different Types Of Surgical Instrument Forceps,Jennings Mouth Gag Product on Alibaba.com

10PCS Muti-Types Fetish BDSM Sex Restraint Kit Games Erotic Accessories Couples Lace Collar Mouth Gag Handcuffs Sex Toys | Wish

Glycosaminoglycan Neutralization in Coagulation Control | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology

Bioanalysis

A Bit of Advice: Gag bits | HORSE NATION

Gag - Wikipedia
Posting Komentar untuk "different types of gags"